Comparing the DR5000 to an YD7001, one sees the following benefits:
- Mixed protocol environment possible, e.g. WLANmaus and HandyApp via Z21 and Traincontroller via Xpressnet, WDP or iTrain via LocoNet LAN.
- Use of LAN for Tool and MRR Software, as many have problems with USB.
- More WLAN clients than before.
- Feedback is no longer eaten away when using app and control software at the same time.
- USB stabilised with e.g. iTrain, WDP etc.
- New control panel that can be freely configured.
- DCCext signal control
- Loco functions up to 64
- Pom accessory decoder with corresponding hardware
- Distinction between emergency off and emergency stop without track voltage off.
- Indication of which connection to the YD7001 is currently active by green colouring of the corresponding COM port or the IP
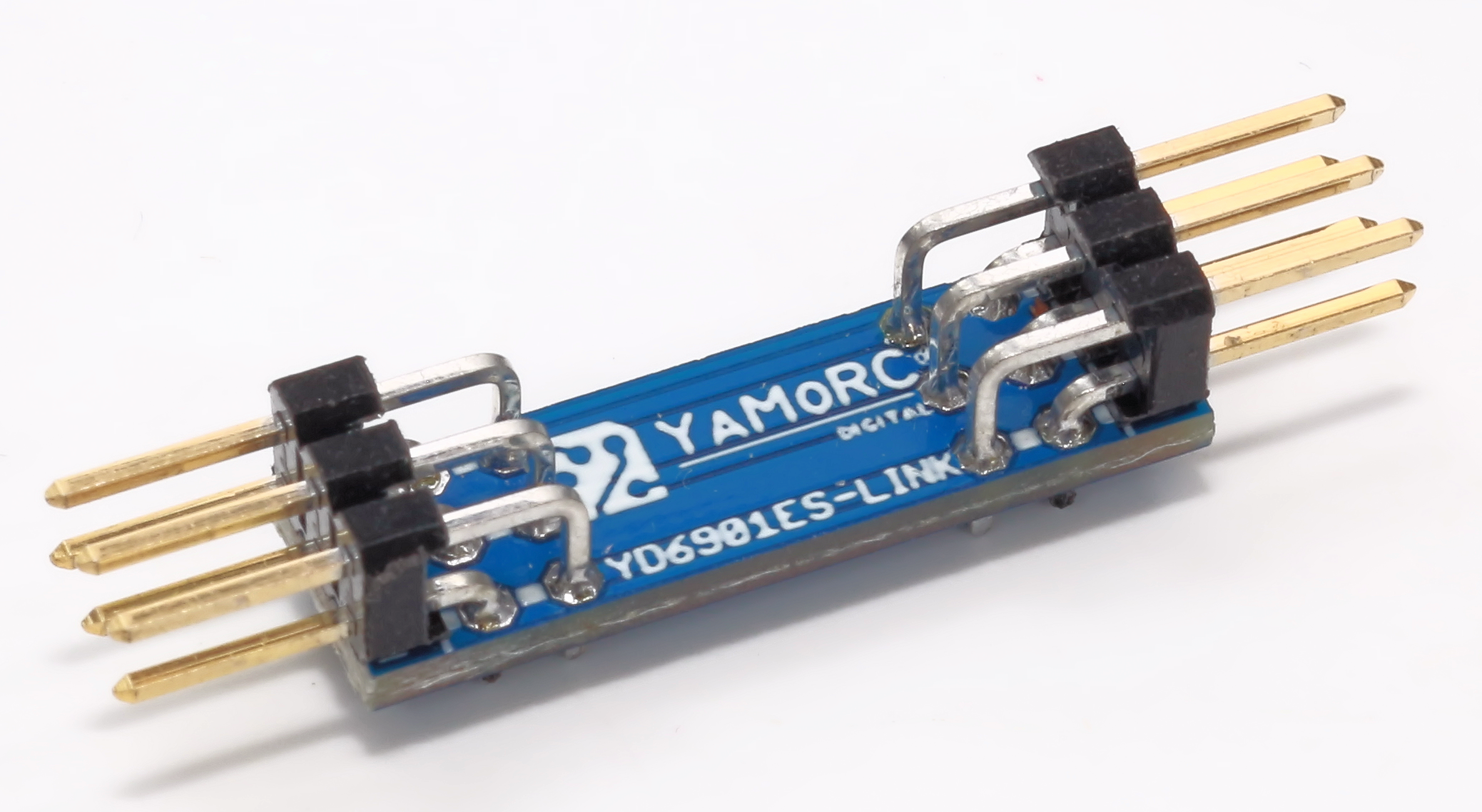
- ES-Link functionality
- Improved feedback monitor both visually and technically (for example, the bell function)
- Guaranteed software maintenance
- Genuine technical support
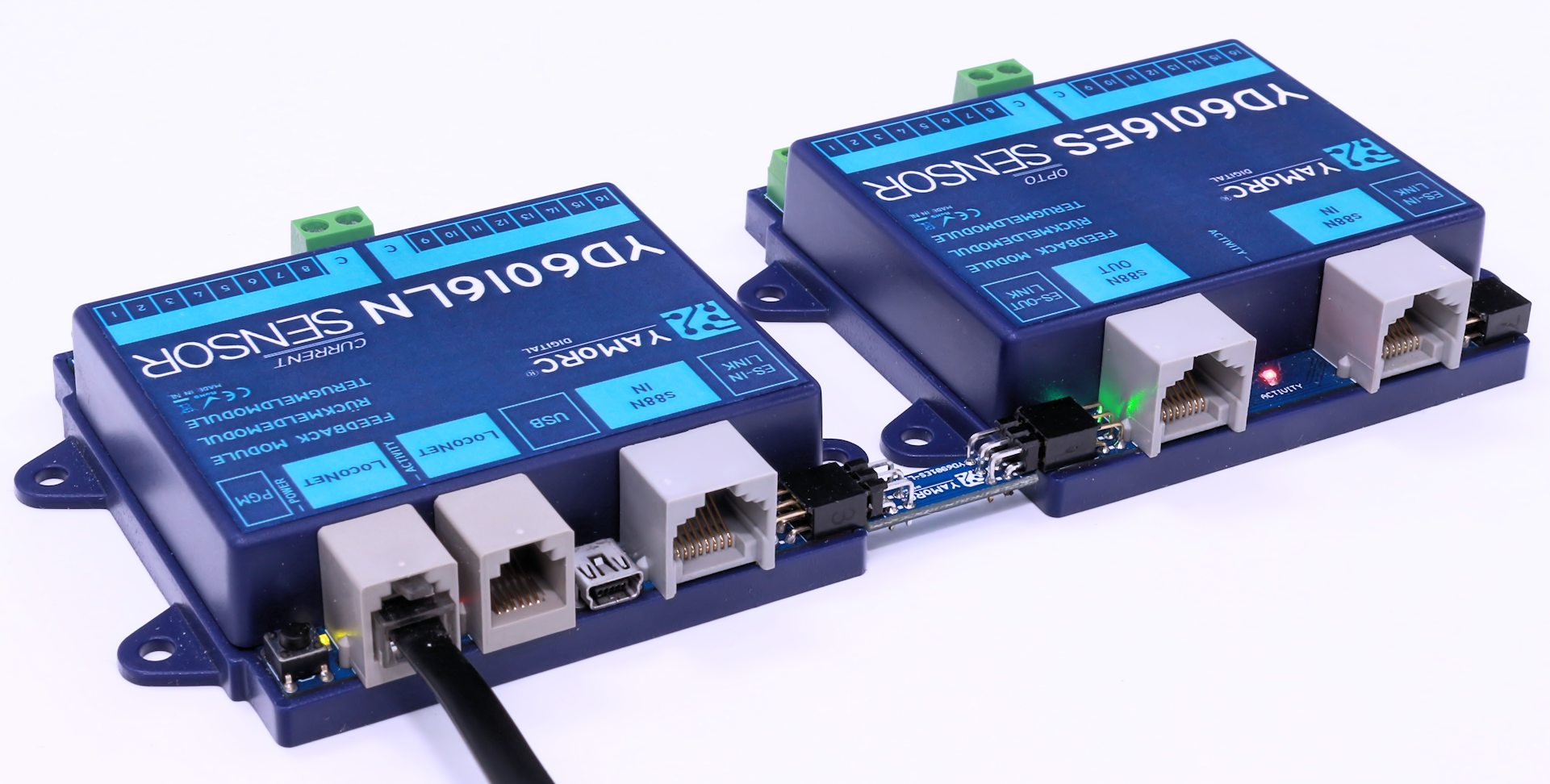
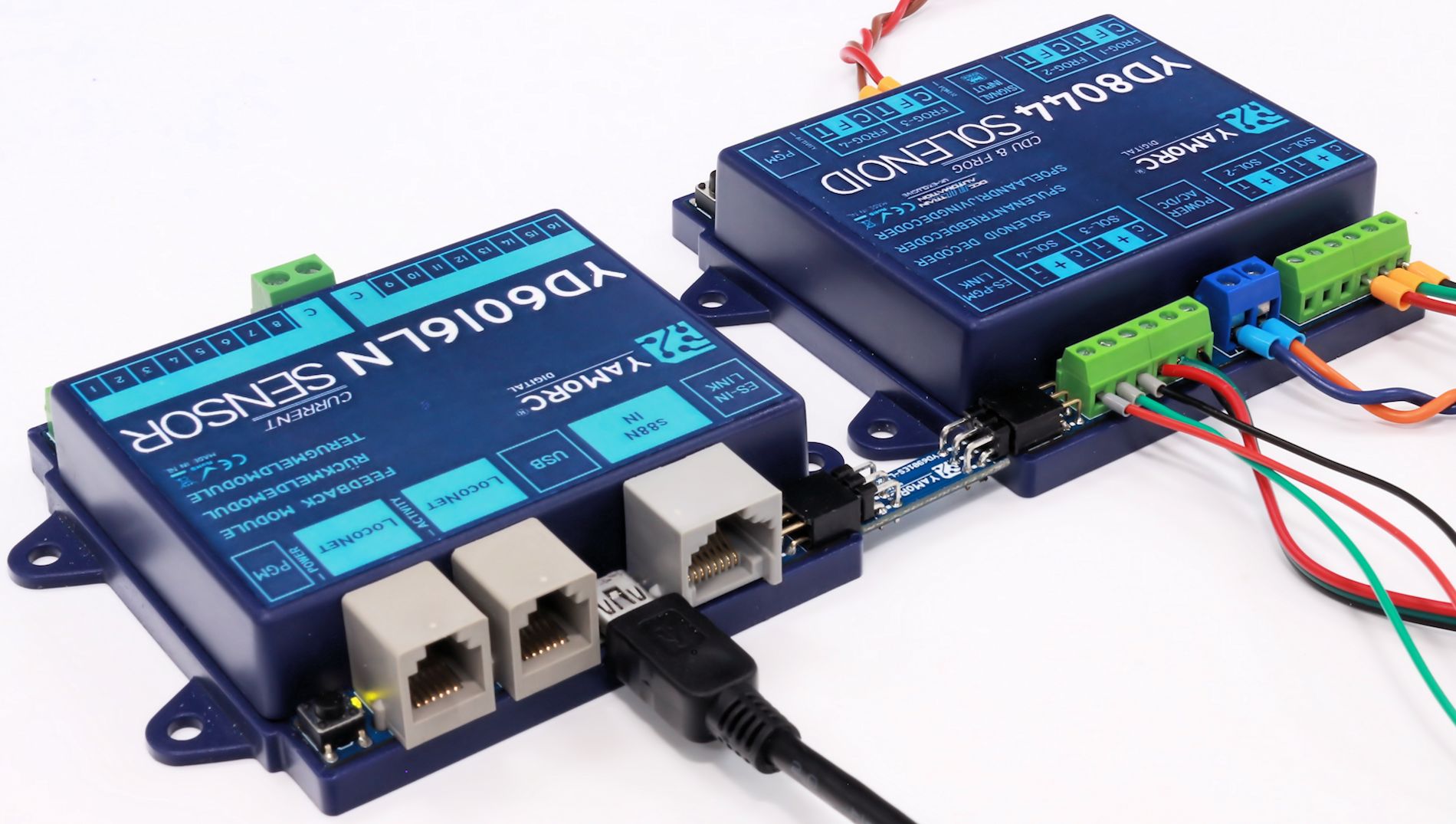
 This comes in handy at the moment one e.g. wants to create a 32, 48 or larger input LocoNet feedback module by combining YD6016LN with multiple YD6016ES feedback modules.
This comes in handy at the moment one e.g. wants to create a 32, 48 or larger input LocoNet feedback module by combining YD6016LN with multiple YD6016ES feedback modules.